22 KiB
| layout | description | permalink |
|---|---|---|
| learn | Learn about the Android SDK | /:collection/:path.html |
Android DApps
{:.no_toc}
This tutorial is written for readers who are new to either or both Blockstack and Android to create a decentralized application. It contains the following content:
- TOC {:toc}
This tutorial was extensively tested using Android Studio 3.1 on a MacBook Air
running High Sierra 10.13.4. If your environment is different, you may encounter
slight or even major discrepancies when performing the procedures in this
tutorial. Please join the Blockstack community
Slack and post questions or comments to
the #support channel.
Finally, this tutorial is written for all levels from the beginner to the most experienced. For best results, beginners should follow the guide as written. It is expected that the fast or furiously brilliant will skip ahead and improvise on this material at will. Fair journey one and all.
If you prefer, you can skip working through the tutorial all together. Instead, you can download the final project code and import it into Android Studio to review it.
Understand the sample application flow
When complete, the sample application is a simple hello-world display. It is
intended for user on an Android phone.
Only users with an existing blockstack.id can run your
final sample application. When complete, users interact with the sample
application by doing the following:
Set up your environment
This sample application has two code bases, a Blockstack hello-blockstack
application and a hello-andriod Android application. Before you start
developing the sample, there are a few elements you need in your environment.
Install Android Studio
If you are an experienced Android developer and already have an Android development environment on your workstation, you can use that and skip this step. However, you will need to adjust the remaining instructions for your environment.
Follow the installation instructions to download and Android Studio 3.1 for your operating system. Depending on your network connection, this can take between 15-30 minutes.
Do you have Node.js?
Node.js v10 or higher is recommended the minimum supported version is Node.js v8. Before you begin, verify you have the correct version of Node.js and its tools installed.
$ node -v
v12.10.0
$ which npm npx
/usr/local/bin/npm
/usr/local/bin/npx
If you don't have these installed, take a moment to install or upgrade as needed.
Install the Blockstack test rig
Users interact with Blockstack-enabled applications through a web browser. You
can Blockstack in test mode, on localhost or you can interact with completed
apps through the Blockstack webapp which is available at
[https://browser.blockstack.org/].
If you have already installed Blockstack for testing locally and have an existing Blockstack ID, skip this section. Otherwise, continue onto install Blockstack.
-
Go to Blockstack
-
Install the version appropriate for your operating system.
Build the Blockstack hello-world
In this section, you build a Blockstack hello-world application. Then, you
modify the hello-world to interact with the Android app via a redirect.
Generate and launch your hello-blockstack application
{% include scaffolding.md %}
In this section, you build an initial React.js application called
hello-blockstack.
-
Create a
hello-blockstackdirectory.mkdir hello-blockstack -
Change into your new directory.
cd hello-blockstack -
Use the Blockstack application generator to create your initial
hello-blockstackapplication.$ npx generator-blockstack --react npx: installed 338 in 13.792s create package.json create .gitignore create webpack.config.js create netlify.toml create firebase.json ... I'm all done. Running npm install for you to install the required dependencies. If this fails, try running the command yourself. > fsevents@1.2.9 install /private/tmp/testymc/node_modules/fsevents > node install added 775 packages from 455 contributors and audited 9435 packages in 20.934s found 0 vulnerabilitiesDepending on your environment you may have some warnings with the installation. Optionally, you can fix these before continuing to the next section.
-
Respond to the prompts to populate the initial app.
After the process completes successfully, you see a prompt similar to the following:
[fsevents] Success: "/Users/theuser/repos/hello-blockstack/node_modules/fsevents/lib/binding/Release/node-v59-darwin-x64/fse.node" is installed via remote npm notice created a lockfile as package-lock.json. You should commit this file. added 1060 packages in 26.901s -
Run the initial application.
$ npm run start > hello-blockstack@0.0.0 start /Users/meepers/repos/hello-blockstack > webpack-dev-server Project is running at http://localhost:8080/ webpack output is served from / 404s will fallback to /index.html Hash: 4d2312ba236a4b95dc3a Version: webpack 2.7.0 Time: 2969ms Asset Size Chunks Chunk Names .... Child html-webpack-plugin for "index.html": chunk {0} index.html 541 kB [entry] [rendered] [0] ./~/lodash/lodash.js 540 kB {0} [built] [1] ./~/html-webpack-plugin/lib/loader.js!./src/index.html 533 bytes {0} [built] [2] (webpack)/buildin/global.js 509 bytes {0} [built] [3] (webpack)/buildin/module.js 517 bytes {0} [built] webpack: Compiled successfully.The system opens a browser displaying your running application.
At this point, the browser is running a Blockstack server on your local host. This is for testing your applications only.
-
Choose Sign in with Blockstack
The system displays a prompt allowing you to create a new Blockstack ID or restore an existing one.
-
Follow the prompts appropriate to your situation.
If you are restoring an existing ID, you may see a prompt about your user being nameless, ignore it. At this point you have only a single application on your test server. So, you should see this single application, with your own
blockstack.iddisplay name, once you are signed in:
Add a redirect end point to your application
When a user opens the webapp from the Blockstack Browser on an Android phone, you want the web app to redirect the user to your Android application. The work you do here will allow it.
-
From the terminal command line, change directory to the root of your sample application directory.
-
Use the
touchcommand to add a redirect endpoint to your application.This endpoint on the web version of your app will redirect Android users back to your mobile app.
$ touch public/redirect.html -
Open
redirect.htmland add code to the endpoint.<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Hello, Blockstack!</title> <script> function getParameterByName(name) { var match = RegExp('[?&]' + name + '=([^&]*)').exec(window.location.search); return match && decodeURIComponent(match[1].replace(/\+/g, ' ')); } var authResponse = getParameterByName('authResponse') window.location="myblockstackapp:" + authResponse </script> <body> </body> </html>Blockstack apps are identified by their domain names. The endpoint will receive a get request with the query parameter
authResponse=XXXXand should redirect the browser tomyblockstackapp:XXXX.myblockstackapp:is custom protocol handler. The handler should be unique to your application. Your app's web-based authentication uses this handler to redirect the user back to your Android app. Later, you'll add a reference to this handler in your Android application. -
Close and save the
redirect.htmlfile. -
Ensure your Blockstack compiles successfully.
Create the hello-android project
In this section, you'll create an Android application in Android Studio. You'll run the application in the emulator to test it.
Create a simple project
In this section, you create an inital project. You'll validate the application's iniatial state by creating an emulator to run it in. Open Android Studio and do the following:
-
Open Android Studio and choose Start a new Andriod Studio project.
If studio is already started, choose File > New > New Project.
-
Enter these fields in the Create Android Project page.
Application Name hello-androidCompany domain USERNAME.example.comProject location /Users/USERNAME/AndroidStudioProjects/helloandroidInclude Kotlin support Set (checked) -
Press Next to display Target Android Devices.
-
Check Phone and Tablet.
-
Choose API 27: Andriod 8.1 (Oreo) for the target version.
-
Press Next.
-
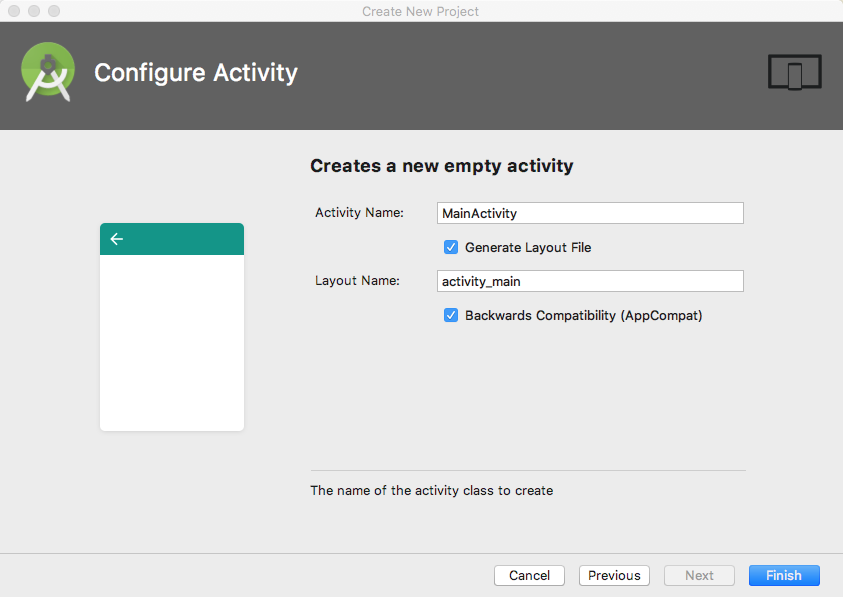
Choose Empty Activity and press Next.
-
Leave the Configure Activity dialog with its defaults.
-
Press Finish.
Android studio builds your initial project. This can take a bit the first time you do it.
Run the app in an emulator
In this section, you run the appliation and create an emulator when prompted.
-
Once the project is imported into studio, click the
appmodule in the Project window. -
Then, select Run > Run (or click the green arrow in the toolbar).
Studio prompts you to Select Deployment Target.
-
Choose Create New Virtual Device and press OK.
Studio prompts you to Select Hardware.
-
Choose a Phone running Pixel XL.
Studio prompts you for a system image.
-
Choose Oreo which is API level 27 and press Next.
Studio asks you to verify your new emulator configuration.
-
Press Finish.
The emulation takes a moment to build. Then, studio launches the emulation and opens your application.
Configure your application with the Blockstack SDK
Now that you have created your initial project and verified it running in an emulator, you are ready to begin configuring the application for use with Blockstack.
-
In studio, open the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile. -
Add an
<intent-filter>with the custom handler for Blockstack.<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:scheme="myblockstackapp" /> </intent-filter> -
Open the Project's
build.gradlefile. -
Add the Jitpack repository
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }to therepositoriessection.When you finish, that section looks like this:
allprojects { repositories { google() jcenter() maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' } } } -
Open the Module
build.gradlefile. -
Set the
defaultConfig minSdkVersionto19.When you are done, you should see (within your own username not
meepers):android { compileSdkVersion 27 defaultConfig { applicationId "com.example.meepers.hello_android" minSdkVersion 19 targetSdkVersion 27 versionCode 1 versionName "1.0" testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" } ... } -
Below this, add the Blockstack Android SDK dependency to your project's
dependencieslist:When you are done you should see:
dependencies { implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:$kotlin_version" implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:27.1.1' implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3' implementation 'com.android.support:design:27.1.1' testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12' androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.2' androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.2' implementation 'com.github.blockstack:blockstack-android:0.4.0' }NOTE: Ignore the warning on the appcompat` dependencies.
-
Sync your project.
Be sure to check the sync completed successfully.
-
Run your app in the emulator.
You've made a lot of changes, make sure the emulator is still running correctly.
Add a simple interface
-
Open the
app/res/layout/activity_main.xmlfile.The
activity_main.xmlfile defines the graphical elements. Some elements are required before you can functionality to yourMainActivity.ktcode. -
Replace the entire content of the file with the following code:
The new interface includes a
BlockstackSignInButtonwhich is provided by the SDK. This SDK includes a themed "Sign in with Blockstack" button (BlockstackSignInButton). You use this button here with theorg.blockstack.android.sdk.ui.BlockstackSignInButtonclass.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <org.blockstack.android.sdk.ui.BlockstackSignInButton android:id="@+id/signInButton" android:layout_width="307dp" android:layout_height="45dp" android:layout_margin="4dp" android:layout_marginEnd="185dp" android:layout_marginStart="39dp" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="16dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/userDataTextView" android:layout_width="370dp" android:layout_height="27dp" tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="6dp" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="70dp" /> </android>This codes adds a button and some text to your application.
-
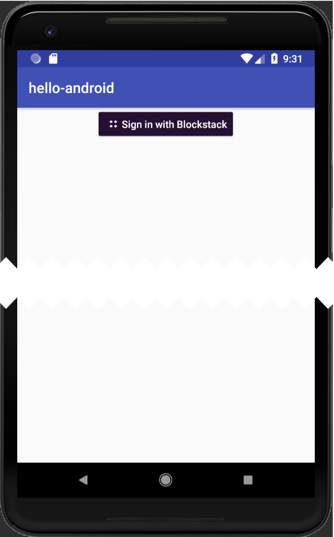
Choose Run > Apply changes.
-
Choose Run > Run app in the emulator.
The emulator now contains a new interface with a button:
Add session & authentication code
-
Open the
MainActivity.ktfile. -
Add some additional imports to the top below the
android.os.Bundleimport.When you are done, your imports should appear as follows:
import android.content.Intent import android.os.Bundle import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity import android.view.View import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.* import org.blockstack.android.sdk.BlockstackSession import org.blockstack.android.sdk.Scope import org.blockstack.android.sdk.UserData import org.blockstack.android.sdk.toBlockstackConfig -
Add a variable for the Blockstack session before
onCreate.class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private var _blockstackSession: BlockstackSession? = null override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } } -
Replace the existing the
onCreatefunction with the following:override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) val scopes = arrayOf(Scope.StoreWrite) val config = "https://flamboyant-darwin-d11c17.netlify.com" .toBlockstackConfig(scopes) _blockstackSession = BlockstackSession(this, config) signInButton.isEnabled = true signInButton.setOnClickListener { view: View -> blockstackSession().redirectUserToSignIn { // only called on error } } if (intent?.action == Intent.ACTION_VIEW) { // handle the redirect from sign in handleAuthResponse(intent) } }This new
onCreatedoes several things:- Define the initial state for the
signInButton. - Supply authentication information for connecting to your Blockstack app:
appDomainandscopes(forredirectURI,manifestURIthe default values are used) - Add a listener for the button click.
Notice that the application in this example is a URI you have not set up. Registering and application name takes time, so in time's interest you'll use an existing app that is identical to the
hello-worldyou created earlier. For a production version, you'll need to replaceappDomain,redirectURI,manifestURIandscopeswith values appropriate for your app. - Define the initial state for the
-
Add a private function to reflect when a user successfully signs in.
private fun onSignIn(userData: UserData) { userDataTextView.text = "Signed in as ${userData.decentralizedID}" signInButton.isEnabled = false } -
Handle sign in requests with an
onNewIntentfunction if the activity was already opened when signing inRetrieve the authentication token from the custom protocol handler call and send it to the Blockstack session.
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent) if (intent?.action == Intent.ACTION_VIEW) { handleAuthResponse(intent) } } -
Create a handler for the authentication response.
private fun handleAuthResponse(intent: Intent) { val response = intent.dataString if (response != null) { val authResponseTokens = response.split(':') if (authResponseTokens.size > 1) { val authResponse = authResponseTokens[1] blockstackSession().handlePendingSignIn(authResponse, { userData -> if (userData.hasValue) { // The user is now signed in! runOnUiThread { onSignIn(userData.value!!) } } }) } } } -
Add the convenience method to access the blockstack session.
fun blockstackSession() : BlockstackSession { val session = _blockstackSession if(session != null) { return session } else { throw IllegalStateException("No session.") } } -
Verify your final
MainActivity.ktcode looks like this:class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private var _blockstackSession: BlockstackSession? = null override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) signInButton.isEnabled = false val scopes = arrayOf(Scope.StoreWrite) val config = "https://flamboyant-darwin-d11c17.netlify.com" .toBlockstackConfig(scopes) _blockstackSession = BlockstackSession(this, config) signInButton.isEnabled = true signInButton.setOnClickListener { view: View -> blockstackSession().redirectUserToSignIn { // only called on error } } if (intent?.action == Intent.ACTION_VIEW) { handleAuthResponse(intent) } } private fun onSignIn(userData: UserData) { userDataTextView.text = "Signed in as ${userData.decentralizedID}" signInButton.isEnabled = false } override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent) if (intent?.action == Intent.ACTION_VIEW) { handleAuthResponse(intent) } } private fun handleAuthResponse(intent: Intent) { val response = intent.dataString if (response != null) { val authResponseTokens = response.split(':') if (authResponseTokens.size > 1) { val authResponse = authResponseTokens[1] blockstackSession().handlePendingSignIn(authResponse, { userData -> if (userData.hasValue) { // The user is now signed in! runOnUiThread { onSignIn(userData.value!!) } } }) } } } fun blockstackSession() : BlockstackSession { val session = _blockstackSession if(session != null) { return session } else { throw IllegalStateException("No session.") } } }
Run the final app in the emulator
-
Choose Run > Apply changes.
-
Choose Run > Run app in the emulator.
-
When you see the application open, choose Sign in with Blockstack.
The system prompts you how to open.
-
Choose Chrome and click ALWAYS.
-
Move through the rest of the Chrome prompts.
The system presents you with your final application.
-
Work through the Blockstack prompts to login.
Where to go next
Congratulations, you've completed your Android app using the Blockstack Android SDK.
Learn more about Blockstack by trying another tutorial.