12 KiB
| layout | description | permalink |
|---|---|---|
| learn | Single-page application with Blockstack | /:collection/:path.html |
Todo List Application Tutorial
{:.no_toc}
In this tutorial, you build the code for and run a single-page application (SPA) with Blockstack and Vue.js. Once the application is running, you take a tour through the applications’ Blockstack functionality. You’ll learn how it manages authentiation using a Blockstack ID and how it stores information associated with that ID using Blockstack Storage (Gaia).
- TOC {:toc}
{% include note.html content="On macOS, Blockstack requires macOS High Sierra. This tutorial was written on macOS High Sierra 10.13.4. If you use a Windows or Linux system, you can still follow along. However, you will need to "translate" appropriately for your operating system. Additionally, this tutorial assumes you are accessing the Blockstack Browser web application via Chrome. The application you build will also work with a local installation and/or with browsers other than Chrome. " %}
If you prefer a video, you can view a video of the tutorial.
Before you begin
The application you build is a Vue.js application that is completely decentralized and server-less. While not strictly required to follow along, basic familiarity with Vue.js is helpful. When complete, the app is capable of the following:
- authenticating users using Blockstack
- posting new statuses
- displaying statuses in the user profile
- looking up the profiles and statuses of other users
For this tutorial, you will use the following tools:
- your workstation's command line
gitto clone the tutorial codenpmto manage dependencies and scripts
The basic identity and storage services are provided by blockstack.js. To test the application, you need to have already registered a Blockstack ID.
Verify you have git installed
This tutorial uses git to clone the tutorial code. Verify you have installed git using the which command to verify.
$ which git
/usr/local/bin/npm
Verify you have npm installed
The tutorial relies on the npm dependency manager. Before you begin, verify you have installed npm using the which command to verify.
$ which npm
/usr/local/bin/npm
If you don’t find npm in your system, install it.
Make sure you have a Blockstack ID
Finally, make sure you have created at least one Blockstack ID. You’ll use this ID to interact with the application.
Task 1: Install the code and retrieve the dependencies
You can clone the source code with git or download and unzip the code from
the
repository.
These instructions assume you are cloning.
-
Install the code by cloning it.
$ git clone https://github.com/blockstack/blockstack-todos -
Change to directory to the root of the code.
$ cd blockstack-todos -
Use
npmto install the dependencies.$ npm install
The Todo application has a basic Vue.js structure. There are several configuration files but the central programming files are in the src directory:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
main.js |
Application initialization. |
App.vue |
Code for handling the authResponse. |
components/Landing.vue |
Code for the initial sign on page. |
components/Dashboard.vue |
Application data storage and user sign out. |
Task 2: Sign into the application
The example application runs in a node server on your local host. In the this section, you start the application and interact with it.
-
Make sure you are in the root of the code base.
$ pwd /Users/moxiegirl/repos/blockstack-todosThis path will be different for you, but double-check the last part to ensure that you're in the directory into which you cloned and in which you ran
npm install. -
Start the application in your local environment.
$ npm run serve
You should see output similar to the following:
98% after emitting CopyPlugin s
DONE Compiled successfully in 5854ms 7:34:28 PM
App running at:
- Local: http://localhost:8080/
- Network: http://192.168.0.12:8080/
Note that the development build is not optimized.
To create a production build, run npm run build.
```
2. Open your local browser to the `http://localhost:8080` URL.
You should see a simple application:

3. Choose **Sign In with Blockstack**.
If you have already signed into Blockstack the application prompts you to select the ID to use. If you aren’t signed in, Blockstack prompts you to:

If the login to the application is successful, the user is presented with the application:

## Task 3: Learn about the sign in process
{% include sign_in.md %}
## Task 4: Decode the authRequest
To decode the token and see what information it holds:
1. Copy the `authRequest` string from the URL.
<img src="{{site.baseurl}}/develop/images/copy-authRequest.png" alt="">
2. Navigate to [jwt.io](https://jwt.io/).
3. Paste the full token there.
The output should look similar to below:
```json
{
"jti": "f65f02db-9f42-4523-bfa9-8034d8edf459",
"iat": 1555641911,
"exp": 1555645511,
"iss": "did:btc-addr:1ANL7TNdT7TTcjVnrvauP7Mq3tjcb8TsUX",
"public_keys": [
"02f08d5541bf611ded745cc15db08f4447bfa55a55a2dd555648a1de9759aea5f9"
],
"domain_name": "http://localhost:8080",
"manifest_uri": "http://localhost:8080/manifest.json",
"redirect_uri": "http://localhost:8080",
"version": "1.3.1",
"do_not_include_profile": true,
"supports_hub_url": true,
"scopes": [
"store_write",
"publish_data"
]
}
```
The `iss` property is a decentralized identifier or `did`. This identifies the user and the user name to the application. The specific `did` is a `btc-addr`.
## Task 5: Under the covers in the sign in code
Now, go to the underlying `blockstack-todo` code you cloned or downloaded. Sign
in and sign out is handled in each of these files:
| File | Description |
|-----------------|-------------|
| `App.vue ` | Handles the `authResponse`. |
| `Landing.vue ` | Generates the `authRequest`. |
| `Dashboard.vue` | Handles sign out. |
The `src/components/Landing.vue` code configures an `AppConfig` object and then uses this to create a `UserSession`. Then, the application calls a [`redirectToSignIn()`](https://blockstack.github.io/blockstack.js#redirectToSignIn) function which generates the `authRequest` and redirects the user to the Blockstack authenticator:
```js
signIn () {
const appConfig = new this.blockstack.AppConfig(['store_write', 'publish_data'])
const UserSession = new this.blockstack.UserSession({ appConfig: appConfig })
UserSession.redirectToSignIn()
}
Once the user authenticates, the application handles the authResponse in the src/App.vue file. :
mounted () {
const UserSession = this.UserSession
if (UserSession.isUserSignedIn()) {
this.userData = UserSession.loadUserData()
this.user = new this.blockstack.Person(this.userData.profile)
this.user.username = this.userData.username
} else if (UserSession.isSignInPending()) {
UserSession.handlePendingSignIn()
.then((userData) => {
window.location = window.location.origin
})
}
},
If blockstack.isUserSignedIn() is true, the user was previously signed in so Blockstack pulls the data from the browser and uses it in our application. If the check on blockstack.UserSession.isSignInPending() is true, a previous authResponse was sent to the application but hasn't been processed yet. The handlePendingSignIn() function processes any pending sign in.
Signout is handled in src/components/Dashboard.vue.
signOut () {
this.UserSession.signUserOut(window.location.href)
}
The method allows the application creator to decide where to redirect the user upon Sign Out:
Task 6: Work with the application
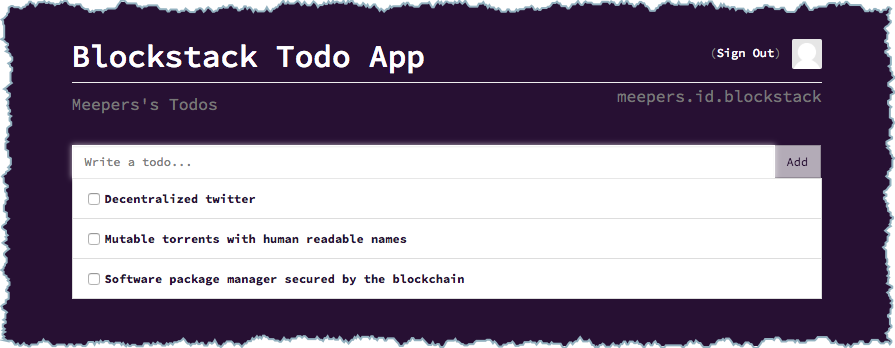
Now, trying adding a few items to the todo list. For example, try making a list of applications you want to see built on top of Blockstack:
Each list is immediately stored in the Gaia Hub linked to your Blockstack ID.
For more information about the Gaia hub, [see the overview in this documentation]({{ site.baseurl }}/storage/overview.html#). You can fetch the todos.json
file you just added by opening the Javascript console and running the following
command:
userSession.getFile("todos.json", { decrypt: true }).then((file) => {console.log(file)})
You should see a JSON with the todos you just added:
[
{
"id":2,
"text":"Software package manager secured by the blockchain",
"completed":false
},
{
"id":1,
"text":"Mutable torrents with human readable names",
"completed":false
},
{
"id":0,
"text":"Decentralized twitter",
"completed":false
}
]
Add another todo and check it off. When you fetch the newly generated file
using the Javascript console, the results reflect your change. Look for "completed":true:
[
{
"id":3,
"text":"Blockstack Todo",
"completed":true
},
{
"id":2,
"text":"Software package manager secured by the blockchain",
"completed":false
},
...
]
Now that you have seen the application in action, dig into how it works.
Task 7: Implement storage
Go to the underlying blockstack-todo code you cloned or downloaded. The
application interactions with your Gaia Hub originate in the
src/components/Dashboard.vue file. First, examine where the changes to the
Todos are processed:
watch: {
todos: {
handler: function (todos) {
const UserSession = this.UserSession
// encryption is now enabled by default
return UserSession.putFile(STORAGE_FILE, JSON.stringify(todos))
},
deep: true
}
},
The todos JSON object is passed in and the
blockstack.UserSession.putFile()
method to store it in a Gaia Hub.
The code needs to read the Todo items from the storage with the blockstack.UserSession.getFile() method which returns a promise:
fetchData () {
const UserSession = this.UserSession
UserSession.getFile(STORAGE_FILE) // decryption is enabled by default
.then((todosText) => {
var todos = JSON.parse(todosText || '[]')
todos.forEach(function (todo, index) {
todo.id = index
})
this.uidCount = todos.length
this.todos = todos
})
},
The todos data is retrieved from the promise.
Summary
{:.no_toc}
You now have everything you need to construct complex applications complete with authentication and storage on the Decentralized Internet. Why not try coding a sample application that accesses multiple profiles.
If you would like to explore the Blockstack APIs, you can visit the Blockstack Core API documentation or the Blockstack JS API.
Go forth and build!