24 KiB
| description |
|---|
| Learn how to implement Gaia in a DApp |
Storage
{:.no_toc}
In this tutorial, you build a micro-blogging application using multi-player Gaia storage. Gaia is Blockstack's decentralized high-performance storage system. The tutorial contains the following topics:
- TOC {:toc}
This tutorial does not teach you about authentication. That is covered in depth in the guide to Blockstack Connect.
{% include note.html content="This tutorial was written on macOS High Sierra 10.13.4. If you use a Windows or Linux system, you can still follow along. However, you will need to "translate" appropriately for your operating system. Additionally, this tutorial assumes you are accessing the Blockstack Browser web application via Chrome. The application you build will also work with a local installation and/or with browsers other than Chrome. " %}
About this tutorial and the prerequisites you need
The storage application you build with this tutorial is a React.js application that is completely decentralized and server-less. While not strictly required to follow along, basic familiarity with React.js is helpful. When complete, the app is capable of the following:
- authenticating users using Blockstack
- posting new statuses
- displaying statuses in the user profile
- looking up the profiles and statuses of other users
The basic identity and storage services are provided by blockstack.js.
For this tutorial, you will use the following tools:
- Node.js v10 or higher is recommended the minimum supported version is Node.js v8.
blockstack.jsto authenticate the user and work with the user's identity/profile information
Before you begin, verify you have the correct version of Node.js and its tools installed.
$ node -v
v12.10.0
$ which npm npx
/usr/local/bin/npm
/usr/local/bin/npx
If you don't have these installed, take a moment to install or upgrade as needed. Also, make sure you have [created at least one Blockstack ID]({{ site.baseurl }}/browser/ids-introduction.html#create-an-initial-blockstack-id). You'll use this ID to interact with the application.
Finally, if you get stuck at any point while working on the tutorial, the completed source code is available for you to check your work against. You can also try out the live build of the app.
Generate and launch the public application
{% include scaffolding.md %}
In this section, you build an initial React application called Publik.
-
Create a the
publikdirectory.mkdir publik -
Change into your new directory.
cd publik -
Use the Blockstack application generator to create your initial
publikapplication.$ npx generator-blockstack --react npx: installed 338 in 13.792s create package.json create .gitignore create webpack.config.js create netlify.toml create firebase.json ... I'm all done. Running npm install for you to install the required dependencies. If this fails, try running the command yourself. > fsevents@1.2.9 install /private/tmp/testymc/node_modules/fsevents > node install added 775 packages from 455 contributors and audited 9435 packages in 20.934s found 0 vulnerabilitiesDepending on your environment you may have some warnings with the installation. Optionally, you can fix these before continuing to the next section.
-
Run the initial application.
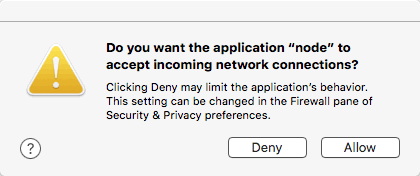
npm run startThe system may prompt you to accept incoming connections.
-
If it does, choose Allow.
-
Your browswer –– Chrome by default –– will open to
http://127.0.0.1:3000/.You should see a simple React app.
-
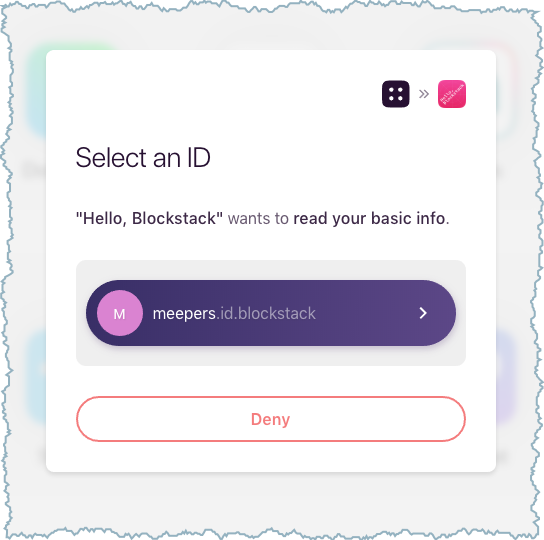
Choose Sign In with Blockstack.
The application tells you it will Read your basic info.
Leave your new application running and move onto the next section.
Add the publish_data scope to sign in requests
Any Blockstack app can use Gaia storage, but those apps that need to share data
publicly must add themselves to the user's profile.json file. The Blockstack
Browser does this automatically when the publish_data scope is requested during
authentication. For this application, the user files stored on Gaia are made
visible to others via the apps property in the user's profile.json file.
Modify your authentication request to include the publish_data scope.
-
Open
src/components/App.jsfile. -
Locate the
AppConfigdeclaration near the beginning of the file.const appConfig = new AppConfig() -
Change it to this:
const appConfig = new AppConfig(['store_write', 'publish_data'])By default, authentication requests include the
store_writescope which enables storage. This is what allows you to store information to Gaia. Adding thepublish_datascope allows your app to share data between users. -
Save your changes.
-
Go back to your app at
http://127.0.0.1:3000/. -
Log out and sign in again.
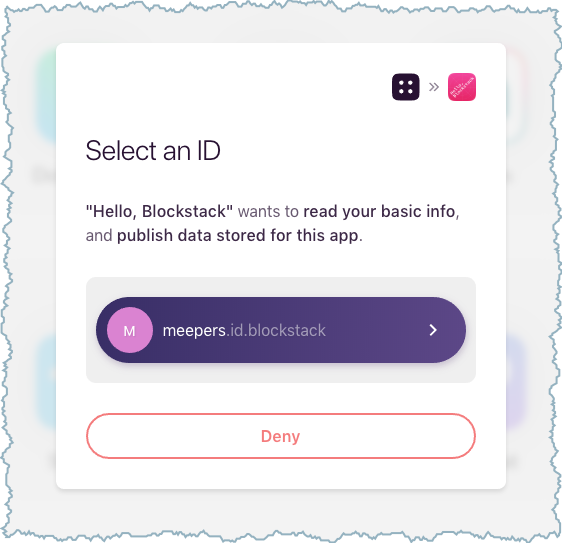
The authentication request now prompts the user for permission to Publish data stored for the app.
Understand Gaia storage methods
Once you authenticate a user with store_write and publish_data, you can
begin to manage data for your users. Blockstack JS provides two methods within
the UserSession class, UserSession.getFile and UserSession.putFile for
interacting with Gaia storage. The storage methods support all file types.
This means you can store markdown, JSON, or even a custom format.
You can create a meaningful and complex data layer using these two methods. Before creating an application, consider fundamental data architecture and make some decisions about how you’re modeling data. For example, consider building a simple grocery list app. A user should be able to create, read, update, and delete grocery lists.
A single file collection stores items as an array nested inside each grocery list:
// grocerylists.json
{
"3255": {
"items": [
"1 Head of Lettuce",
"Haralson apples"
]
},
// ...more lists with items
}
This is conceptually the simplest way to manage grocery lists. When you read a
/grocerylists.json file with getFile(), you get back one or more grocery
lists and their items. When you write a single list, the putFile() method
overwrites the entire list. So, a write operation for a new or updated grocery
list must submit all existings lists as well.
Further, because this runs on the client where anything can go wrong. If the client-side code encounters a parsing error with a user-input value and you could overwrite the entire file with:
line 6: Parsing Error: Unexpected token.
Further, a single file makes pagination impossible and if your app stores a
single file for all list you have less control over file permissions. To avoid
these issues, you can create an index file that stores an array of IDs. These
IDs point to a name of another file in a grocerylists folder.
This design allows you to get only the files you need and avoid accidentally overwriting all lists. Further, you’re only updating the index file when you add or remove a grocery list; updating a list has no impact.
Add support for user status submission and lookup
In this step, you add three blockstack.js methods that support posting of "statuses".
These are the UserSession.putFile, UserSession.getFile, and lookupProfile methods.
-
Open the
src/components/Profile.jsfile. -
Replace the initial state in the component method so that it holds the key properties required by the app.
This code constructs a Blockstack
Personobject to hold the profile. Your component should look like this:export const Profile = ({ userData, handleSignOut }) => { const [newStatus, setNewStatus] = React.useState(''); const [statuses, setStatuses] = React.useState([]); const [statusIndex, setStatusIndex] = React.useState(0); const [isLoading, setLoading] = React.useState(false); const [username, setUsername] = React.useState(userData.username); const [person, setPerson] = React.useState(new Person(userData.profile)); const { authOptions } = useConnect(); const { userSession } = authOptions; // ... } -
Modify the rendered result to add a text input and submit button to the by replacing it with the code below:
The following code renders the
person.nameandperson.avatarURLproperties from the profile on the display:export const Profile = ({ userData, handleSignOut }) => { // ... state setup from before return ( <div className="container"> <div className="row"> <div className="col-md-offset-3 col-md-6"> <div className="col-md-12"> <div className="avatar-section"> <img src={ person.avatarUrl() ? person.avatarUrl() : avatarFallbackImage } className="img-rounded avatar" id="avatar-image" /> <div className="username"> <h1> <span id="heading-name">{ person.name() ? person.name() : 'Nameless Person' }</span> </h1> <span>{username}</span> <span> | <a onClick={ handleSignOut.bind(this) }>(Logout)</a> </span> </div> </div> </div> <div className="new-status"> <div className="col-md-12"> <textarea className="input-status" value={newStatus} onChange={handleNewStatus} placeholder="Enter a status" /> </div> <div className="col-md-12"> <button className="btn btn-primary btn-lg" onClick={handleNewStatusSubmit} > Submit </button> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> ); }This code allows the application to post statuses. It also displays the user's Blockstack ID. To display this, your app must extract the ID from the user profile data.
-
Add two methods in the
Profilecomponent to handle the status input events:const handleNewStatus = (event) => { setNewStatus(event.target.value); } const handleNewStatusSubmit = async (event) => { await saveNewStatus(newStatus); setNewStatus(""); } -
Add a
saveNewStatus()method to save the new statuses.const saveNewStatus = async (statusText) => { const _statuses = statuses let status = { id: statusIndex + 1, text: statusText.trim(), created_at: Date.now() } _statuses.unshift(status) const options = { encrypt: false } await userSession.putFile('statuses.json', JSON.stringify(_statuses), options); setStatuses(_statuses); setStatusIndex(statusIndex + 1); }The default behavior for
putFile()is to encrypt data when storing it, making it unreadable by everyone except the logged in user. In this exampleputFile()call is not encrypting the status because our app is meant to share statuses publicly. -
Save the
Profile.jsfile.After the application compiles successfully, your application should appears as follows:
-
Enter your status in the text box and press the Submit button.
At this point, the status you've just submitted isn't being displayed. In the next section you add code to display the statuses back to the user as a blog entry.
Fetch and display statuses
Update Profile.js again.
-
Go back to the
render()method. -
Locate the
<div className="new-status">containing the text input and Submit button. -
Right before the matching closing
</div>element in this section, add this block.<div className="col-md-12 statuses"> {isLoading && <span>Loading...</span>} {statuses.map((status) => ( <div className="status" key={status.id}> {status.text} </div> ))} </div>This displays existing state. Your code needs to fetch statuses on page load.
-
Add a new method called
fetchData()after thesaveNewStatus()method.const fetchData = async () => { setLoading(true); const options = { decrypt: false } const file = await userSession.getFile('statuses.json', options) const _statuses = JSON.parse(file || '[]') setStatusIndex(_statuses.length); setStatuses(_statuses); setLoading(false); }By default,
getFile()this method decrypts data; because the defaultputFile()encrypts it. In this case, the app shares statuses publicly. So, there is no need to decrypt. -
Call
fetchData()from the by using React'suseEffectmethod, which will fetch data whenever the component's username state is changed..// after setting up your component's state React.useEffect(() => { fetchData(); }, [username]); -
Save the file.
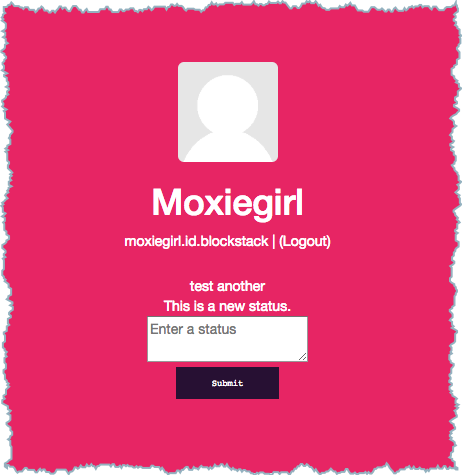
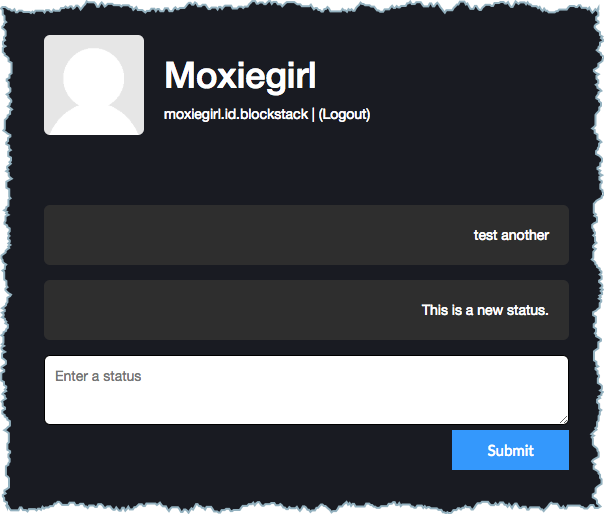
After the application compiles successfully, users are able to Submit multiple statuses and review them in the app.
Change the style
-
Edit the
src/styles/style.cssfile. -
Replace the content with the following:
/* Globals */ a,a:focus,a:hover{color:#fff;} html,body{height:100%;text-align:center;background-color:#191b22;} body{color:#fff} .hide{display:none;} .landing-heading{font-family:'Lato',Sans-Serif;font-weight:400;} /* Buttons */ .btn{font-family:'Lato',Sans-Serif;padding:0.5625rem 2.5rem;font-size:0.8125rem;font-weight:400;line-height:1.75rem;border-radius:0!important;-webkit-transition:all .2s ease-in-out;-moz-transition:all .2s ease-in-out;-ms-transition:all .2s ease-in-out;-o-transition:all .2s ease-in-out;transition:all .2s ease-in-out;-webkit-user-select:none;-moz-user-select:none;-ms-user-select:none;user-select:none;} .btn-lg{font-size:1.5rem;padding:0.6875rem 3.4375rem;line-height:2.5rem;} .btn:focus,.btn:active:focus,.btn.active:focus{outline:none;} .btn-primary{color:#fff;border:1px solid #2C96FF;background-color:#2C96FF;} .btn-primary:hover,.btn-primary:focus,.btn-primary:active{color:#fff;border:1px solid #1a6ec0;background-color:#1a6ec0;} /* Avatar */ .avatar{width:100px;height:100px;} .avatar-section{margin-bottom:25px;display:flex;text-align:left;} .username{margin-left:20px;} /* Scaffolding */ .site-wrapper{display:table;width:100%;height:100vh;min-height:100%;} .site-wrapper-inner{display:flex;flex-direction:column;justify-content:center;margin-right:auto;margin-left:auto;width:100%;height:100vh;} .panel-authed{padding:0 0 0 0;} /* Home button */ .btn-home-hello{position:absolute;font-family:'Source Code Pro',monospace;font-size:11px;font-weight:400;color:rgba(255,255,255,0.85);top:15px;left:15px;padding:3px 20px;background-color:rgba(255,255,255,0.15);border-radius:6px;-webkit-box-shadow:0px 0px 20px 0px rgba(0,0,0,0.15);-moz-box-shadow:0px 0px 20px 0px rgba(0,0,0,0.15);box-shadow:0px 0px 20px 0px rgba(0,0,0,0.15);} /* Input */ input, textarea{color:#000;padding:10px;} .input-status{width:100%;height:70px;border-radius:6px;} .new-status{text-align:right;} /* Statuses */ .statuses{padding-top:30px;} .status{margin:15px 0px;padding:20px;background-color:#2e2e2e;border-radius:6px} -
Save and close the
src/styles/style.cssfile.After the application compiles, you should see the following:
At this point, you have a basic micro-blogging app that users can use to post and view statuses. However, there's no way to view other users' statuses. You'll add that in the next section.
Lookup user profiles
Let's now modify the Profile.js file to display profiles of other users. You'll
be using the lookupProfile() method that you added to the import statement
earlier. lookupProfile() takes a single parameter that is the Blockstack ID of
the profile and returns a profile object.
Add a new route
Make some changes to the routing structure of your app so that users can view
other users' profiles by visiting http://127.0.0.1:3000/other_user.id
-
Edit the
src/components/App.jsfile. -
Add the new route by importing the
SwitchandRoutecomponents fromreact-router-dom:import { Switch, Route } from 'react-router-dom' -
Locate this line below in the
render()method:: <Profile userSession={userSession} handleSignOut={ this.handleSignOut } /> -
Replace it with the following:
: <Switch> <Route path='/:username?' render={ routeProps => <Profile userSession={userSession} handleSignOut={ this.handleSignOut } {...routeProps} /> } /> </Switch>This sets up a route and captures the route path in the URL as the profile lookup username.
-
Save and close the the
src/components/App.jsfile.
Add in lookupProfile
You also need to add a rule to your app's webpack config so that you can properly
process URL paths that contain the . (dot) character for example,
http://localhost:8080/other_user.id
NOTE: In a production app, you must ensure the web server is configured to handle this.
-
Open the
src/components/Profile.jsfile. -
Expand the
import from blockstackstatement to include thelookupProfilemethod.Add
lookupProfileafterPerson.When you are done, the import statement should look like the following:import { Person, lookupProfile } from 'blockstack'; -
Add a single method to the
Profileclass that determines if the app is viewing the local user's profile or another user's profile.// Make sure you add this new prop! export const Profile = ({ userData, handleSignOut, match }) => { // ... const isLocal = () => { return match.params.username ? false : true } // ... }You use
isLocal()to check if the user is viewing the local user profile or another user's profile. If it's the local user profile, the app runs thegetFile()function you added in an earlier step. Otherwise, the app looks up the profile belonging to theusernameusing thelookupProfile()method. -
Modify the
fetchData()method like so:const fetchData = async () => { setLoading(true); if (isLocal()) { const options = { decrypt: false } const file = await userSession.getFile('statuses.json', options) const _statuses = JSON.parse(file || '[]') setStatusIndex(_statuses.length); setStatuses(_statuses); setLoading(false); } else { const username = match.params.username try { const newProfile = await lookupProfile(username) setPerson(new Person(newProfile)); setUsername(username); } catch (error) { console.log('Could not resolve profile'); } } }NOTE: For
httpsdeployments, the default Stacks Node API endpoint for name lookups should be changed to point to a core API served overhttps. Otherwise, name lookups fail due to browsers blocking mixed content. Refer to the Blockstack.js documentation for details. -
Add the following block to
fetchData()right after the call tosetUsername(username)block:const options = { username: username, decrypt: false } const file = await userSession.getFile('statuses.json', options) const _statuses = JSON.parse(file || '[]') setStatusIndex(_statuses.length); setStatuses(_statuses); setLoading(false);This fetches the user statuses.
Finally, you must conditionally render the logout button, status input textbox, and submit button so they don't show up when viewing another user's profile.
-
Replace the returned JSX in the
Profilecomponent with the following:return ( <div className="container"> <div className="row"> <div className="col-md-offset-3 col-md-6"> <div className="col-md-12"> <div className="avatar-section"> <img src={ person.avatarUrl() ? person.avatarUrl() : avatarFallbackImage } className="img-rounded avatar" id="avatar-image" /> <div className="username"> <h1> <span id="heading-name">{ person.name() ? person.name() : 'Nameless Person' }</span> </h1> <span>{username}</span> {isLocal() && <span> | <a onClick={handleSignOut}>(Logout)</a> </span> } </div> </div> </div> {isLocal() && <div className="new-status"> <div className="col-md-12"> <textarea className="input-status" value={newStatus} onChange={handleNewStatus} placeholder="What's on your mind?" /> </div> <div className="col-md-12 text-right"> <button className="btn btn-primary btn-lg" onClick={handleNewStatusSubmit} > Submit </button> </div> </div> } <div className="col-md-12 statuses"> {isLoading && <span>Loading...</span>} {statuses.map((status) => ( <div className="status" key={status.id}> {status.text} </div> ))} </div> </div> </div> </div> );This checks to ensure that users are viewing their own profile, by wrapping the Logout button and inputs with the
{isLocal() && ...}condition.
Put it all together
-
Stop the running application in terminal by sending a CTRL-C.
-
Restart the application so that the disabling of the
.(dot) rule takes effect.npm run start -
Point your browser to
http://127.0.01:3000/your_username.id.blockstackto see the final application.
Wrapping up
Congratulations, you are all done! We hope you've enjoyed learning a bit more about Blockstack.